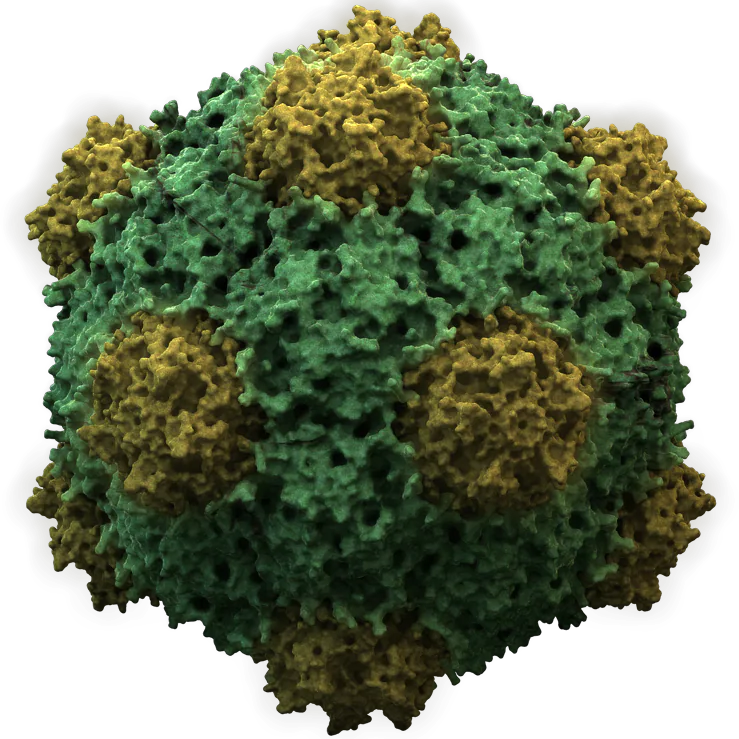
Cowpea Mosaic Virus
Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV) is a non-enveloped plant virus of the comovirus group. Infection of a susceptible cowpea leaf causes a "mosaic" pattern in the leaf, and results in high virus yields (1-2 g/kg). Its genome consists of 2 molecules of positive-sense RNA (RNA-1 and RNA-2) which are separately encapsidated. Both RNA1 and RNA2 have a VPg (virus genome-linked protein) at the end, and polyadenylation at the end. Genomic RNA1 and RNA2 are expressed by a polyprotein processing strategy. RNA1 encodes helicase, VPg, protease and RdRp. RNA2 encodes movement protein and coat protein. The virus particles are 28 nm in diameter and contain 60 copies each of a Large (L) and Small (S) coat protein. The structure is well characterised to atomic resolution, and the viral particles are thermostable. The identification of the virus is attributed to Lister and Thresh in 1955, but it is now known as a variant of the Sunn-hemp mosaic virus.